A Comprehensive Guide to AI in Business
What is AI?
Artificial intelligence - or AI - is a broad term that refers to the development of computer systems that can perform functions normally associated with the human brain such as learning, analysing, reasoning, generating content and interacting with the world around it.
AI systems are designed to analyse vast amounts of data, learn from patterns and experiences, and make informed decisions or predictions. Machine learning, natural language processing, computer vision, and robotics all fall under the umbrella of artificial intelligence.
The current AI boom revolves around generative AI and language models, but AI has actually been around for decades. Think less T-1000 and more Siri and Alexa, IBM’s Watson, or Richard Wallace’s A.L.I.C.E (Artificial Linguistic Internet Computer Entity) chatbot.
The Difference Between Traditional AI and Generative AI
If Chat GPT rather than Watson springs to mind when thinking about AI, that may be because of the buzz currently generated by generative AI (no pun intended). Within the realm of AI, generative is basically the next generation, but traditional AI is still important to know and harness in your business.
Traditional AI is also known as classic AI or conventional AI, it focuses on performing tasks according to specific rules or programming. It takes data, analyses it, and then makes decisions or predictions. Systems like chatbots, SEO, fraud detection, and even voice assistants would fall under this category.
Generative AI, on the other hand, focuses specifically on the creation, or generation, of new content. Generative AI systems can produce text, images, music, and even code. Chat GPT, Google Bard, Bing Chat - these systems are often trained using extensive datasets of existing content, where they learn patterns and rules that are subsequently used to create new (for all intents and purposes) content.
So, in essence, the fundamental distinction between traditional AI and generative AI lies in their respective purposes. While conventional AI systems are mainly designed to understand and analyse information, generative AI systems are engineered to generate new information.
Recognizing the difference between these two branches of AI provides a clearer understanding of their distinct roles and capabilities. While traditional AI offers powerful insights and predictions derived from data analysis, generative AI provides a creative edge by generating content based on learned patterns. Together, they present huge possibilities, fueling innovation and enabling businesses to leverage the power of intelligent technology for both understanding and creation.
How AI Works
Ok, we now know that, at its core, AI aims to develop systems that can simulate human intelligence and perform tasks that typically require human cognitive abilities, let’s look at how AI actually works.
In straightforward terms, AI operates by merging extensive datasets with intuitive processing algorithms. AI then refines these algorithms through the acquisition of behavioural patterns found within the dataset.
Picture AI as a comprehensive toolkit, capable of solving problems and suggesting potential outcomes.
It's crucial to grasp that AI is far from a single algorithm—it's an intricate machine-learning ecosystem that wields the power to tackle challenges and offer informed insights. Let’s take a look at each of the steps that make AI tools like chatbots, data analysis, and content generation possible.
📊 Step 1: Data Input - Laying the Groundwork
At the very beginning, AI collects all sorts of information – numbers, words, pictures, and more. This raw material becomes the building blocks of AI's understanding. However, the challenge is sorting through this mix of data to pick out what really matters.
🤔 Question: How does AI sift through this jumble of information to find the important bits?
⚙️ Step 2: Data Processing - Shaping Information
Once the data is gathered, AI goes to work on it. It's like tidying up a messy room – AI organizes, arranges, and transforms the raw data into something that makes sense. This process takes all the scattered bits and turns them into useful insights.
🤔 Question: How does AI's processing transform a bunch of numbers and words into meaningful information?
🧠 Step 3: Machine Learning - The Learning Phase
Now, AI starts learning from the processed data. It's like how we learn from our experiences. AI looks for patterns and connections within the information. It uses these patterns to create models that can predict things, put stuff into groups, and make choices. And the more it learns, the better it gets at it.
🤔 Question: How does AI get better at things by looking at the patterns it finds in the data?
🔗 Step 4: Neural Networks - Layered Computation
Neural networks are a bit like puzzles with many pieces. Each piece does a small job, and together they solve bigger problems. In AI, these networks are made up of layers that work together to process information. It's a bit like teamwork – each layer does its thing, and the final result is a smarter AI.
🤔 Question: How do these layered networks work together to make AI smarter at solving complicated problems?
💬 Step 5: Natural Language Processing (NLP) - Understanding Human Language
NLP teaches AI how to talk to people. It's like teaching a new language to a friend. With NLP, AI can understand what people say, translate languages, and even guess how someone is feeling just from what they write. This helps AI communicate and understand us better.
🤔 Question: How does NLP teach AI to understand what we say and write, just like we do?
🔮 Step 6: Decision-Making - Guided Decision-Making
In this phase, AI puts its learning to good use. It's a bit like when we weigh the pros and cons before making a decision. AI looks at different choices, predicts what might happen with each choice, and suggests the best one based on what it knows. It's like having a really smart friend who gives great advice!
🤔 Question: How does AI decide what's the best thing to do based on what it's learned from data?
Conclusion
🌟 As we wrap up our journey through AI's inner workings, we're left in awe of how machines can think and learn. From collecting data to making smart choices, AI's path shows us a world where intelligence has endless possibilities.
🤖 Question: Are you ready to explore the AI world further and see how it's always getting smarter?
The Four Concepts Of AI
AI isn't just a single entity; it's a mosaic of capabilities that reflect human thinking. Not every tool or platform will work for your business, but there are four main concepts to remember when working with AI in any setting: Reactive Machines, Limited Memory, Theory of Mind, and Self-Awareness. These concepts peel back the layers, showing us how AI's journey unfolds.
Reactive Machines
At the heart of AI's evolution lies the concept of Reactive Machines. These systems operate based on pre-programmed rules and patterns, responding to specific inputs with predefined outputs. Just like a script that follows a specific sequence of actions, reactive machines can excel in narrowly defined tasks. However, they lack the ability to learn from new experiences or adapt to dynamic situations.
Imagine a chess-playing AI that knows all the rules and moves but lacks the capability to improve over time. Reactive machines are the foundation of AI's journey, providing the initial groundwork for more advanced capabilities.
Limited Memory
The concept of Limited Memory takes AI a step further by introducing the ability to learn from past experiences. These machines can retain a certain amount of information about previous interactions, allowing them to make more informed decisions over time. This is akin to humans learning from past mistakes or successes to shape future choices.
Limited Memory AI systems can be likened to recommendation engines that suggest products or content based on previous user interactions. This concept brings AI closer to human-like adaptability by using memory as a guide for decision-making.
Theory of Mind
Theory of Mind encapsulates the idea of AI understanding not only its environment but also the intentions and beliefs of other entities. In human terms, it's the ability to recognise that others have thoughts, emotions, and desires of their own. AI systems embracing this concept can predict and understand the behaviour of individuals based on their presumed mental states.
Imagine an AI that can anticipate your preferences and intentions, not just based on your past behaviour, but by recognising your underlying motivations. This concept represents a significant leap toward machines emulating human-like social interactions and empathy.
Self-Awareness
The pinnacle of AI's journey is the concept of Self-Awareness. Just as humans possess self-awareness, machines embracing this concept would understand their own existence, capabilities, and limitations. This goes beyond understanding and predicting others' intentions; it involves introspection and consciousness about the AI's own state.
While we're not at the point of AI achieving true self-awareness as humans do, the concept challenges us to envision a future where machines possess a sense of identity and understanding of their own role.
As we continue our journey through the landscapes of AI, these concepts beckon us to explore how the boundaries of intelligence are constantly being pushed, creating a future where machines evolve into something far beyond mere tools.
In this section
AI in Business
Ok, now that we have a foundational understanding of what AI is, how it works, and the concepts guiding its evolution, we want to look at AI in a business context. It is in this area that we have seen AI evolve quickly past traditional boundaries, enabling organizations to unlock new possibilities, enhance productivity, and gain a competitive edge. AI in a business context involves using AI technologies and techniques to enhance various aspects of business operations, decision-making, and customer interactions.
We will look at specific examples and industries in our next section, but generally we can see that AI is transforming business through data analysis and insights, offering the ability to extract valuable patterns and trends from vast datasets, both structured and unstructured. These insights empower data-driven decision-making, process optimization, and the discovery of untapped opportunities. Moreover, AI contributes to delivering personalized customer experiences by analyzing customer data, understanding preferences, behaviors, and purchasing patterns. This tailored approach enhances customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.
In addition to data-driven insights and personalized experiences, AI revolutionizes business operations by automating repetitive tasks, reducing errors, and improving efficiency. Intelligent robotic process automation (RPA) systems handle routine, rule-based activities, freeing human resources for more strategic endeavours. Furthermore, AI's prowess in processing large datasets and identifying patterns makes it invaluable for predictive analytics and forecasting.
By leveraging historical data and machine learning models, organizations gain the capability to make precise predictions regarding market trends, demand fluctuations, and customer behaviour. This foresight empowers businesses to optimize inventory, anticipate market changes, and make informed strategic decisions. Lastly, AI aids in decision-making by providing real-time insights and predictive capabilities. Its algorithms can analyze complex scenarios, assess multiple variables, and generate recommendations based on historical data and predefined criteria. This support helps leaders make informed, timely decisions, manage risks, and seize opportunities.
While it's useful to see how AI works for business at a high level, it's just as valuable to see examples of how AI is changing the business landscape for specific industries and departments.
How Does AI Benefit Businesses?
AI has already made significant changes to the business landscape, and it’s certainly showing no signs of slowing down. As AI evolves, it will undoubtedly drive innovation, impacting the way in which businesses operate and how they can deliver value to their customers. Here are just a few of the ways AI is already changing the business world:
Improved Decision Making
AI technologies, such as machine learning and data analytics, help businesses process vast amounts of data to gain valuable insights. This enables data-driven decision-making across various aspects of the business, from sales and marketing to supply chain management. So what previously might have taken a full day of meetings to analyse, discuss and make decisions, could now be resolved in minutes using AI.
Personalisation and Customer Experience
AI will now be able to predict what customers need, even before they do. This can be done by analysing all customer data and recommending products or services tailored to individual preferences, taking out any of the guesswork that was previously done by humans. So for example, before AI, someone would have manually set up email workflows recommending different products or services they think would complement that specific customer segment best, based on previous transactions and customer behaviour. AI can now remove the human guesswork involved in this and analyse all of the data to recommend the products that have the highest chance of being purchased, based on actual data. This can help lead to increased revenue, enhanced customer experiences and increased customer loyalty.
Process Automation
AI-powered automation has been revolutionising the way businesses operate. Tasks that were once performed manually can now be automated, leading to increased efficiency, reduced errors, and cost savings. For example, AI can be used in the recruitment process to narrow down candidates. The AI can perform data analysis on all job applications and can eliminate unsuitable candidates, leaving the ones that are most qualified for the job. This can massively increase productivity as previously this may have taken someone hours to manually analyse.
Chatbots and Customer Support
AI-driven chatbots have become commonplace in customer support, providing immediate responses to customer queries and improving response times, even outside regular business hours. The chatbots can use conversational AI to simulate a discussion with a customer and use natural language, making it less obvious that it’s a bot. Chatbots can save businesses as much as 30% on their customer support costs.

Source: Venture Beat
Supply Chain Optimisation
Managing a supply chain is complex, often difficult work, involving coordinating multiple parties and considering factors such as availability of materials, labour, price fluctuations and much more. AI has transformed this process as it can manage large amounts of supply chain data, analyse and identify trends and predictions about future concerns.
AI enables businesses to better manage their supply chains by predicting demand, optimising inventory levels, and streamlining logistics and transportation. Forecasting capacity constraints and customer demand is essential to successfully managing a supply chain, and AI can be trained to do both tasks with efficiency.
Predictive Maintenance
It can be difficult to detect potential equipment malfunctions with the human eye. In industries like manufacturing and aviation, AI can provide a helping hand by predicting equipment failures before they even occur. Businesses can use these insights to plan ahead for repairs to ensure equipment is kept running smoothly, resulting in less downtime and increased operational efficiency.
Fraud Detection and Security
AI-based algorithms can identify suspicious activities and patterns, helping businesses detect and prevent fraudulent transactions and improving overall cybersecurity. For example, machine learning can use historical data labelled as fraudulent or non-fraudulent and use anomaly detection algorithms to identify transactions that are significantly different from the norm based on given features.
Job Losses and New Business Models and Industries
Without a doubt, some jobs may be replaced entirely by AI or dramatically impacted. Office administrative support, legal, architecture and engineering, marketing, sales and financial operations are just some of the sectors that could be at high risk, but there is still large potential for it to create entirely new business models and industries such as autonomous vehicles, personalised medicine, and AI-powered financial advisory services.
It's essential to note that the widespread adoption of AI also raises ethical and social implications, including concerns about job displacement, privacy issues, biases in algorithms, and the responsible use of AI technology.
AI for Customer Service
Customer service can use AI in various ways to enhance efficiency, improve customer experience, and streamline processes, which helps lead to increased customer loyalty and retention. It’s vital however that AI enhances customer service and doesn’t replace the human aspect of it altogether.
Here are some examples of how AI can be used in customer service:
Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle routine customer enquiries and provide instant responses 24/7, meaning customer service agents can work fewer hours or focus on other high-priority tasks. The chatbots can answer frequently asked questions, assist with basic troubleshooting issues and direct customers to the appropriate resources. AI can also provide real-time language translation, enabling businesses to communicate effectively with customers from different linguistic backgrounds.
Sentiment Analysis and Customer Feedback
AI can analyse customer interactions to determine the sentiment behind their messages. This helps customer service teams gauge customer satisfaction, identify potential issues, and prioritise urgent cases. AI can also analyse feedback from various sources, including social media and online surveys, to gain insights into customer preferences and pain points.
Personalisation
AI can analyse customer data and interactions to offer personalised product recommendations and tailored solutions, making customers feel valued and understood.
Voice Assistants
AI-powered voice assistants can assist customers via phone calls, making it easier for them to access information or perform tasks without human intervention.
Automated Ticketing and Routing
AI can automatically assign and route customer queries to the right support agents, ensuring faster response times and better issue resolution.

Source: Dashly
AI for Sales
Sales teams can leverage AI in several ways to boost productivity, improve sales processes, and increase revenue. Here are some ways sales teams can utilise AI:
Lead Scoring and Qualification
AI can analyse historical data and customer behaviour to score and prioritise leads based on their likelihood to convert. This helps sales teams focus their efforts on the most promising opportunities rather than wasting time on ones unlikely to convert.
Sales Forecasting
AI can analyse past sales data and market trends to generate accurate sales forecasts, allowing sales teams to make informed decisions and set achievable targets based on real data.
Personalised and Segmented Sales Outreach
AI can analyse customer data to tailor sales messages and content according to individual preferences, increasing the chances of engagement and conversion. It can also segment customers based on various criteria such as buying behaviour, demographics and preferences enabling sales teams to target specific groups with tailored offerings.
Automated Email Flows
AI-powered tools can automate sales emails, sending personalised and timely messages to prospects and customers, nurturing leads throughout the sales funnel.
Sales Process Optimisation
AI can analyse the sales process to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies, enabling sales teams to streamline their workflows and optimise their approach.
Chatbots for Sales Support
AI-powered chatbots can assist potential customers during their buying journey, answering questions, offering product recommendations, and guiding them through the sales process.
Upselling and Cross-selling Opportunities
AI can analyse customer data to identify upselling and cross-selling opportunities, helping sales teams suggest relevant products or services to existing customers. AI can also analyse market demand and competitor pricing to adjust product prices in real time, helping sales teams optimise pricing strategies and maximise profitability.
By incorporating AI into their sales processes, sales teams can improve efficiency, accuracy, and customer engagement. It enables them to focus on high-value tasks, make data-driven decisions, and build stronger relationships with customers, ultimately driving revenue growth and achieving better results overall. The human side is still an integral part to sales however so be mindful that to build long-lasting relationships with your customers, not every aspect of the sales process can be driven by AI.
Audience Segmentation and Targeting
AI can analyse vast amounts of customer data to identify patterns and segment audiences based on demographics, interests, behaviour, and preferences. This enables marketers to deliver highly targeted and personalised messages to specific customer groups. It can also score leads based on their likelihood to convert, helping marketers prioritise efforts on the most promising prospects and improve lead nurturing strategies.
Content Creation and Curation
AI-driven tools can generate content, including blog posts, social media updates, and product descriptions, based on predefined guidelines. AI can also curate relevant content from various sources to share with the audience. In our experience, using AI to get started with content creation is best but it definitely needs fact checked, edited and adjusted to make it more human and relatable to your audience. You can also use AI tools to optimise your content for better search engine rankings, improving your organic traffic and visibility. AI tools can also analyse search trends and optimise content for better search engine rankings, improving organic traffic and visibility. It can help marketers narrow down vast amounts of data to identify relevant keywords that will be most valuable for target audiences and competition. AI can also analyse existing content and provide insights into how to improve it for better SEO performance.
Chatbots for Customer Engagement
Not one of the newest creations from AI, but one that is still highly effective for marketers is AI-powered chatbots. They can help nurture leads and engage with website visitors and social media users in real time, answering questions, providing support, and guiding customers through their buying journey.
Personalisation and Product Recommendations
AI can deliver personalised product recommendations and content based on individual customer preferences, increasing the likelihood of conversion and enhancing customer experience. Previously, marketers would have manually had to analyse the data themselves to determine the best up-sells and cross-sells, but now AI can do it for them, so customers can be targeted with the right product options based on purchase history.
Email Marketing Automation
AI can optimise email marketing campaigns by automating send times, subject lines, and content based on individual user behaviour and preferences. It can also automate A/B testing, identifying the most effective variations and continuously optimising performance based on real-time data.
Accurate Forecasting
AI models can analyse historical sales data, market trends, and external factors to provide accurate demand forecasts. By predicting future demand accurately, businesses can optimise their inventory levels, plan ahead for any periods of high or low demand and tailor their marketing campaigns accordingly. AI can also analyse customer behaviour to adjust pricing and promotional offers in real time, optimising sales and revenue.
Ad Targeting and Bidding
AI-powered advertising platforms can optimise ad targeting and bidding strategies, ensuring that ads are shown to the most relevant audience and achieving better ROI.
By embracing AI technologies, marketers can streamline processes, improve efficiency, and deliver more personalised experiences to customers. AI-driven insights can guide strategic decisions, increase marketing ROI, and ultimately lead to stronger customer engagement and loyalty. It's crucial, however, to ensure that AI is used ethically and responsibly, respecting user privacy and maintaining transparency in its applications.
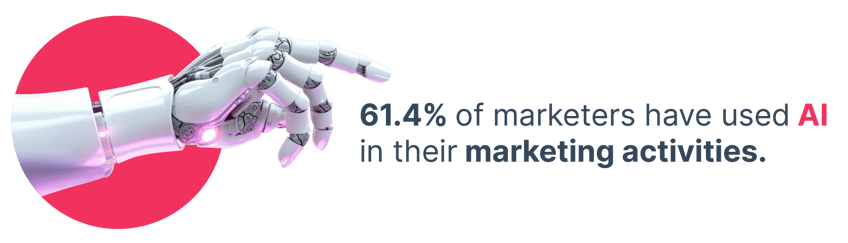
Source: Influencer Marketing Hub
Further reading: AI is Not Killing Marketing (Yet)
Idea Generation
AI can analyse vast amounts of data from various sources to identify trends, customer preferences, and market gaps. This can help teams brainstorm and generate new product ideas and refine existing ones based on real-time insights. AI can also use data on how similar products and features are performing within the marketplace to ensure there is sufficient demand for the new product.
Concept Testing and Validation
AI-powered surveys and sentiment analysis can gauge consumer reactions and preferences toward different product concepts, allowing teams to validate ideas before investing significant resources. AI-driven design tools can also assist in creating more efficient and aesthetically pleasing product designs. Generative design, for instance, can explore numerous design variations based on specified constraints.
Prototyping and Simulation
Usually creating a prototype of a product to test is one of the most time-consuming aspects of the product development process. AI can create prototypes in just a few hours, which could be the difference between success and failure for some smaller businesses with fewer resources to spare. AI can simulate product behaviour in various conditions, aiding in identifying potential issues and refining prototypes before physical manufacturing. AI can generate and instantly visualise new ideas and various variations of each. This can save time and resources in the development process.
Supply Chain and Inventory Management
AI can optimise supply chain operations by predicting demand, improving inventory management, and enhancing procurement processes. This reduces costs and ensures products are available when needed.
Predictive Maintenance
For products that require maintenance, AI can predict when equipment might fail, allowing teams to perform maintenance before a breakdown occurs. This can improve product reliability and customer satisfaction
Quality Control and Defect Detection
AI can use predictive analytics to anticipate potential defects and predict the quality of a product based on the data generated and analysed during the manufacturing process. AI-powered computer vision can inspect products for defects to ensure they meet quality standards at speeds and efficiency not capable of humans.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) for Customer Feedback
Most product teams rely on surveys or focus groups to collect feedback, taking a lot of time and resources to manually analyse. Now, NLP-powered AI can analyse customer reviews, feedback, and online conversations to gain insights into product strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement. You can essentially find out what features your customers are talking about the most and what customers' feelings are on these, and use this to refine your product.
AI can also help tailor products to individual customer preferences by analysing data and generating personalised recommendations. This enhances the customer experience and can lead to higher customer satisfaction.
Incorporating AI into product development can lead to faster innovation, improved decision-making, reduced costs, and increased customer satisfaction. However, it's essential to carefully plan and implement AI solutions to ensure they align with the team's goals and the target market's needs.
Challenges and Limitations of AI
The Potential for Bias in AI Systems
The potential for bias in AI systems is a significant concern and has garnered a lot of attention in recent years. Bias in an AI context refers to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in the decisions made by AI. These unjust decisions aren’t being made consciously by the AI itself of course, but from the data that has been provided to the AI for learning and training in the design of the algorithms themselves. Since it is humans who provide the data to the AI to learn from, it can be easy to unconsciously provide them with data that is biased. These biases can then be unintentionally replicated and amplified in the AI predictions or actions.
Bias in AI can manifest in various ways, for example favouring specific demographic groups, perpetuating stereotypes or producing unjust results. Addressing bias in AI involves identifying, understanding, and mitigating these biases to ensure fair and unbiased decision-making.
Some examples of bias in AI include:
Gender Bias: Some language models have shown gender biases, associating certain professions or roles more strongly with one gender than another. This can affect chatbots, virtual assistants, and automated content generation, reinforcing stereotypes. For example, when some virtual assistants are asked about nurses, the AI has been shown to refer to them as female, while a doctor may be referred to as male which can further reinforce stereotypes that already exist in society. These biases occur because the data used to train the algorithm reflects historical biases and are not fully up to date.
Facial Recognition Bias: Facial recognition systems have been found to have higher error rates when identifying people with darker skin tones, women, and older individuals. This bias can lead to misidentification and privacy concerns, particularly for marginalised groups. This bias arguably raises serious concerns as it can cause misidentifications and disparities in the treatment of individuals during security screenings, access control or law enforcement. This bias is usually caused by the imbalance of racial groups contained within the datasets used to train the AI, which results in reduced accuracy and fairness in identifying certain groups. To address this bias, the training data needs to be diversified to ensure accurate recognition of all ethnicities.
Criminal Justice Bias: Predictive policing algorithms use historical crime data to forecast future likely crime hotspots. So location-based algorithms can link places, events and historical crime rates to predict where and when crimes are likely to take place. This means police may target specific areas which can lead to certain communities being over-policed, and under-resourced policing for areas that might actually require it.
Other AI tools use data on people’s age, gender, marital status, substance abuse and criminal record to predict who has a chance of being involved in future criminal activity. This data can easily be skewed by arrest rates to create biased, unfair outcomes. According to the US Department of Justice Figures, you are more than twice as likely to be arrested if you are Black than if you are white, and a black person is 5 times more likely to be stopped without just cause than a white person. So if this is the type of data being used to train the algorithms, then it undoubtedly creates bias in the policing system. Mitigating this bias involves the implementation and accountability measures to ensure the AI algorithm's predictions do not contribute to further disparities in the criminal justice system.
Hiring and Recruitment Bias: AI-based hiring tools can unintentionally favour certain demographics, leading to biased hiring decisions. If historical hiring data is skewed, AI can learn and perpetuate those biases. For example, if historical hiring practices favoured male candidates for specific roles, the AI might inadvertently discriminate against female candidates, creating a gender imbalance in the workplace.
Credit Scoring Bias: AI-driven credit scoring models use various factors to assess individuals' creditworthiness and can disadvantage certain groups if training data reflects past discriminatory lending practices. This can lead to unequal access to unequal access to loans, mortgages, and financial opportunities. For instance, the AI model can assign lower credit scores to individuals from certain racial or ethnic backgrounds based on past disparities in lending access. To address this bias, it's essential to ensure that training data is diverse, representative, and free from discriminatory patterns, to create fair and equitable credit scoring models.
Healthcare Disparities: AI is increasingly used in healthcare to diagnose diseases and recommend treatment plans. The algorithm however might favour certain racial or socioeconomic groups due to biased training data. For example, studies show that people with low incomes have a higher health risk than people with high incomes. If the data is only collected from an expensive private clinic, then the AI model will become biased. Likewise, if the data provided to the AI doesn’t include an equal split of genders, the output can be inaccurate. This is because different diseases and illnesses affect men and women differently.
Online Advertisements Bias: AI-driven ad targeting can reinforce stereotypes by showing ads for high-paying jobs more often to men than women or displaying certain products predominantly to specific racial or ethnic groups. For instance, if historical data shows that certain job roles have traditionally attracted more applicants of a specific gender, the algorithm might optimise ad delivery based on those patterns. As a result, the algorithm could disproportionately show ads for high-paying or leadership roles to one gender while displaying ads for support or administrative roles to another.
These examples illustrate how biases in AI systems can arise from various sources, including biased training data, algorithm design, and societal prejudices. It's crucial to address these biases to ensure that AI technologies are fair and equitable, and serve the best interests of all users and stakeholders.
The Security and Privacy Risks of AI
The integration of AI into various aspects of modern life brings transformative benefits but also introduces substantial privacy and security risks. As AI systems rely heavily on data, often personal or sensitive in nature, the collection, storage, and processing of vast amounts of personal information raise concerns about data breaches and unauthorised access. Businesses must prioritise data privacy and protection, adhering to relevant regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). Ensuring transparency in data usage and obtaining informed consent from users is essential to maintain trust and ethical standards. And it’s important to remember, that everything you provide to AI will be stored and used for future training. Personal data like names, addresses and contact details can be inadvertently and easily collected during normal day-to-day interactions with AI This data is all saved within the AI meaning there is a risk of unintentionally generating sensitive information that violates privacy regulations, putting individuals at risk.
Research by Cyberehaven found that:
- 11% of data that employees paste into Chat GPT is confidential
- 4% of employees have pasted sensitive data into it at least once

Source: Cyberhaven
So with such personal information being shared on sites like Chat GPT and Bard, there are serious security risks to consider. Say, for example, a company has an AI-driven chatbot to handle customer support inquiries. That chatbot stores everything it’s given, which will likely include customer information such as names, addresses, card details and purchase history to be able to provide personalised assistance. Depending on the security measures in place, this data can very easily be hacked, raising concerns of privacy and potential identity theft. AI systems need strong encryption, access controls and regular security checks to ensure that confidential information is not accessed and customer privacy is maintained.
AI tools themselves need to have strong security measures in place to mitigate the risk of model poisoning. This is when malicious data or code is manipulated into the training data to compromise the AI models’ functionality, causing it to produce malicious results and outcomes that would be harmful when deployed. These attackers can also initiate more subtle forms of manipulation, known as bias injection. These attacks can be especially harmful in industries such as healthcare, automotive and transportation.
Another security concern is the ever-growing number of security measures that are controlled by voice and facial recognition. AI presents an opportunity for hackers to create deep fakes and audio prompts to be able to trick security systems into verifying identities and accessing personal and company information. Using just four minutes of audio, an Australian journalist at The Guardian, was able to generate a clone of their own voice to gain access to Centrelink accounts, which holds sensitive material such as financial information and important personal documents.
The Ethical Implications of AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming the way businesses operate, however, this technological advancement also brings with it a host of ethical considerations that cannot be overlooked. Alongside the issues discussed above, it’s important for businesses to consider the following:
Automated Decision-Making and Accountability: AI systems often make autonomous decisions, raising questions about accountability. When things go wrong, determining who is responsible can be challenging. This ethical grey area requires businesses to establish clear protocols for attributing responsibility and ensure that human oversight is maintained, especially in critical decisions. Businesses should maintain transparency, making it possible to explain AI's actions and allowing for recourse when things go wrong.
Job Displacement: AI automation may lead to job displacement in some industries. Businesses must ethically address the impact on employees by investing in reskilling and upskilling programs and adopt some strategies to mitigate the impact of job displacement including:
- Reskilling and upskilling: Businesses can provide training programs and resources to help employees gain new skills that are in demand in the evolving job market. Training programs can be tailored to the specific needs and interests of employees, taking into account their current skills and future career goals.
- Create new roles: This might not always be possible but try to identify areas within the organisation where AI and automation can create new opportunities and roles, and actively develop these positions.
- Collaborate with educational institutions: Partner with local colleges and universities to develop training programs that align with the skills needed in the job market. Consider offering financial incentives to employees pursuing further education or training. Encourage existing employees to participate in pursuing further education and allow flexibility within their role to facilitate their new learning.
Environmental Impact: The environmental footprint of AI, particularly in terms of energy consumption, is a growing concern. AI, especially deep learning models, requires extensive computational power, leading to high energy consumption. Training large AI models can be as energy-intensive as running several households for months. Businesses must explore sustainable AI solutions and adopt eco-friendly practices, such as optimising algorithms for efficiency and using renewable energy sources for AI infrastructure.
The pace of AI hardware development and innovation can also result in the rapid obsolescence of equipment, leading to the generation of electronic waste (e-waste). This type of waste poses environmental challenges when not properly disposed of or recycled, as it can contain hazardous materials.
Further reading: AI Ethics: What You Need to Know
What are the Top Trends in AI for Businesses?
As AI continues to evolve rapidly, there are certain trends that are gaining the most traction. These include:
Generative AI
This has taken the world by storm recently, not surprising given its ability to generate natural, almost almost-human-sounding language. User-friendly AI models for creating text, images and audio are more popular than ever, with tools like Chat GPT and Google Bard dominating the market. We don’t expect this trend to slow down anytime soon as the tools are constantly evolving and being refined for more effective use in business.
An AI study by Capterra found that 33% of marketers are using AI-based software for copywriting or content generation, with 82% of them reporting that “content generated by AI or ML software is just as good (or better!) than human-generated content.”
Low Code Tech
Historically, lack of coding ability and skills have created a barrier of entry for many companies who need specific software developed for their product or service. This resulted in many businesses using external developers and specialised teams, which is neither efficient or cost-effective. As a result of this, low-code or no-code AI tools are helping businesses to easily leverage machine learning in innovative ways such as designing web services or customer-facing apps. Many drag-and-drop options are available now helping businesses overcome the challenges previously posed by coding language With 50% of medium-to-large companies adopting low-code development, it will drastically reduce the dependency on IT development and support teams.
Human-AI collaboration
With the new and continued technologies emerging, it can be a nerve-wracking time for employees fearing that AI will be able to take over their jobs. There is still value in keeping a human element within many business processes, so the trend of human-AI collaboration is growing. Companies that deploy machines with built-in AI for repetitive or physically demanding tasks can reallocate the human resources to more specialised ones.
Sustainable AI - Most companies now are under pressure to be sustainable and reduce their carbon footprint. And while the technology needed to train a single deep-learning model can result in the emission of 284,000 KG of CO2, it also has the potential to help companies build products, services in a more energy-efficient way and to promote sustainability across various industries and operational domains. Computer vision, for example, in combination with satellite imagery, is used to detect deforestation and unauthorised logging activities in rainforests, along with monitoring illegal fishing practices that harm ocean biodiversity. With the climate crisis worsening, we expect to see a continued effort to implement AI projects focused on addressing critical global issues, rather than solely pursuing corporate profit growth.
How can Businesses Prepare for the Future of AI?
Preparing for the future of AI is crucial for businesses to remain competitive and relevant in an increasingly AI-driven world. Here are some steps that businesses can take to get ready:
Understand AI
Begin by educating yourself and your team about what AI is, what it can and cannot do, and how it can be applied in your industry. This foundational knowledge will help you make informed decisions about AI adoption. Make sure you recognise that AI adoption may require changes in workflows and processes. Implement change management strategies to ensure a smooth transition.
Identify Use Cases
Determine how AI can benefit your business. Identify specific use cases where AI can improve efficiency, reduce costs, or create new revenue streams. Start with small-scale, practical, achievable projects to test ideas and concepts rather than attempting massive transformations straight away. These experiments can help you learn and adapt without committing to a full-scale implementation. For example, consider how AI can enhance customer interactions and experiences. Chatbots, personalisation, and predictive analytics can all be used to improve customer engagement.
Data Collection and Quality
AI relies on data. Ensure that your data is collected, stored, and managed properly. It should be clean, well-structured, and easily accessible. Data privacy and security should also be a priority.
Invest in Talent
Attract and retain AI talent. Hire data scientists, machine learning engineers, and AI specialists who can develop, implement, and maintain AI solutions. Training existing employees in AI skills is also a valuable investment.
AI Strategy
Develop a clear AI strategy that aligns with your business objectives. Determine how AI will fit into your overall business plan and what ROI you expect from your AI initiatives.
Collaborate and Partner
Explore collaborations with AI startups, research institutions, or established tech companies. Partnerships can provide access to expertise, technologies, and resources that may be otherwise challenging to acquire.
Ethics and Regulations
Stay informed about AI ethics and regulations in your industry and region. Ensure that your AI systems are transparent, fair, and compliant with relevant laws and guidelines.
Cybersecurity
With the increased use of AI comes an increased risk of cyber threats. Invest in robust cybersecurity measures to protect your AI systems and the data they rely on.
Continuous Learning
AI is a rapidly evolving field. Encourage a culture of continuous learning within your organisation to keep up with the latest developments and trends. The AI landscape is also extremely dynamic so be flexible and adaptable in your approach to AI adoption, as new technologies and opportunities may emerge.
Monitor ROI
Continuously track the return on investment (ROI) of your AI projects. If a project isn't delivering the expected results, be prepared to adjust or terminate it.
Remember that AI is not a one-size-fits-all solution, and its impact will vary depending on your industry and business model. The key is to approach AI adoption strategically and thoughtfully, with a focus on long-term sustainability and growth.
Conclusions
AI in business is a potent force of transformation, one that promises to reshape the way businesses operate, innovate, and connect with their customers. As we navigate the current state of AI in business, it's evident that this technology is far from reaching its peak.
We can see, as we look to the future, that AI will not merely automate tasks but will serve as a strategic partner to human ingenuity. The collaboration between AI and human expertise will become the cornerstone of business strategies, amplifying the capacity to solve complex problems, make informed decisions, and create value in ways previously unattainable.
Moreover, the ethical use of AI will - and has already started to - become of paramount importance. The responsible deployment of AI systems, characterized by fairness, transparency, and bias mitigation, will be essential to ensure equitable benefits across industries and societies.
AI in business is not a destination but a dynamic journey into an ever-evolving future. It's a realm where the boundaries of what's possible continually expand, and the pioneers who harness AI's potential will undoubtedly lead the charge in shaping tomorrow's business landscape. So, as we conclude this exploration, we stand at the threshold of a future powered by innovation, ethics, collaboration, and the limitless possibilities of AI.
Contributors:

Ashleigh McCabe
Content Marketing Specialist
.jpg?width=2448&height=2448&name=CYMERA_20210218_133809%20(1).jpg)
Melissa Hugel
Content Marketing Manager

Jonny Robinson
Graphic Designer
From Our Blog
Stay up to date with what is new in our industry, learn more about the upcoming products and events.

How to Measure Brand Awareness: 7 Metrics to Track

ROAS vs ROI: 7 Key Differences



